Oral surgery
Dental surgery (or oral surgery) focuses on the following:
- extraction of erupted teeth
- root residues
- teeth included or semi-included in the jaw bones
- endodontic surgery (apicoectomy), i.e. removal of the apex of the teeth involved in the inflammatory processes and subsequent endodontic sealing
- removal of cysts and tumours of the oral cavity
- pre-prosthetic and pre-implant surgery: sinus elevations, i.e. sinus floor elevation using bone grafts, biomaterials or bone reconstructive surgery.
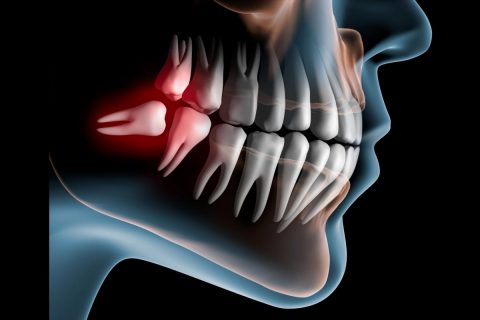
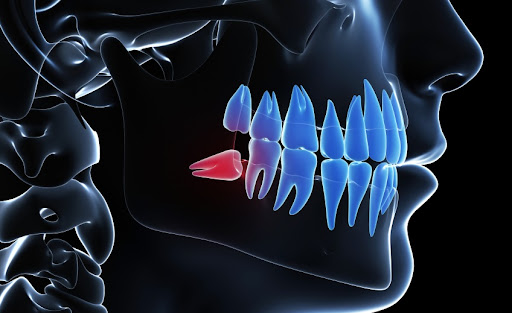
A standard procedure in oral surgery involves extracting wisdom teeth or impacted teeth in general. Abnormal eruption of these teeth can lead to infection, pain, or damage to neighbouring elements.
Oral surgery treatments can involve conscious sedation to ensure a more comfortable experience to the patient.
Questions
Wisdom teeth: what is the ideal age to remove them?
Third molars or wisdom teeth should be checked from the age of 14-16. An early assessment of the space available for the appropriate eruption of the third molars can be done even at this early age. The examination involves radiographic techniques, specifically orthopantomography and computed tomography (CBCT).